
|
In the past three decades, a new crop of entrepreneurs rose to fame and incomparable wealth. Growing from garage-based startups, these mega-wealthy entrepreneurs inspired many others to try their hand at invention and strike out on their own.
The following guide contains key business terms for entrepreneurs. From accounts payable to venture capital, this list includes must-know terms for anyone contemplating the leap into entrepreneurship.
In the most general terms, entrepreneurship simply means having one's own business. But at its heart, true entrepreneurship is inventive and risky, involving creating a new business for a product or market that does not already exist.
Entrepreneurs study markets carefully to find gaps in customer needs, then brainstorm products and services to fill those gaps. Starting with an original business idea, they take it from concept to reality by carefully planning the necessary investments, production, marketing and sales.
Entrepreneurs can work alone or with partners, but there is always a substantial investment of ideas, time, reputation, and money. Entrepreneurship comes with significant risks, but — if successful — it pays out significant rewards.
Whether pitching to investors or training human resources, it's important for entrepreneurs to understand every aspect of running a business. As such, they need to be masters in business jargon and corporate speak. The key terms below will help business owners understand their obligations and navigate the path to success.
Accounts payable refers to unpaid invoices the company owes its suppliers and service providers. It can also refer to the department responsible for paying outstanding invoices.
Accounts payable may include rent, utility bills, office supplies, accounting services, design services, production materials, production labor, equipment, transportation, and more.
The only expense not included in accounts payable is payroll.
Accounts receivable refers to unpaid invoices customers owe the company for goods already received or services already rendered. It can also refer to the department responsible for collecting payment for outstanding invoices.
Adopters are customers who purchase your product or technology. Adopters fall into five groups based on how quickly they use new products:
Early adopters are the most vocal group and often serve as "influencers" to motivate subsequent customers. When marketing a new product, companies often focus on early adopters.
Angel investors are wealthy individuals who invest money in business ventures and early-stage startups that show great promise. In exchange for their investment, angel investors often request a percentage of ownership in the company to make back their investment once the company is successful.
The advantage of finding this type of investor is that you don't have a loan to repay since you give them ownership shares in exchange for the capital. Most angel investors also act as mentors and champions of businesses they invest in because they only make back their investment if the company is successful.
The disadvantage of angel investors is that you have to give away a percentage of your company; some investors want as much as 50%. And with a percentage of shares, many angel investors expect to have a significant say in startup management.
Assets are items of value owned by the company. These can include things like computers, furniture, equipment, inventory, company vehicles, real estate, cash reserves, investments, or intellectual property.
B2B stands for business-to-business and refers to marketing and sales between businesses. Some examples of this are a national clothing chain selling uniforms to the NFL or a software company selling software to a business for employee use.
B2C stands for business-to-consumer and refers to marketing and sales between a business and individual customers. For instance, a national clothing chain might sell workout gear to a gym enthusiast, or a software company might sell software to a student for personal use.
Bootstrapping is when an entrepreneur starts a company with personal finances and little capital. This allows the owner to maintain complete control of the company, but it can financially strain them and their business.
A business model outlines how a company will create and deliver value to its customers. A strong business model will define a business's core purpose, identify target market demographics in-depth, outline corporate structure to meet customer needs, and carefully detail ways to make a profit. Business models need to be carefully and thoroughly prepared, often referred back to, and updated as the business grows and further defines its purpose.
Business models focus on core concepts and goals. To delve into more detail (especially finances), entrepreneurs may also create a business plan, which can help them:
Both a business model and a business plan are important in order to secure financial backing. While angel investors may want a business model that thoroughly and passionately defines the business goals, banks and financial institutions often require a business plan as part of a business loan application.
A business model canvas is a visual chart outlining the basic building blocks needed to start a business. It serves as the framework for a fully developed, in-depth business model.
A business model canvas consists of nine basic building blocks:
A business venture is a new business formed at some risk with the expectation of making a profit.
Cash flow is the movement of money, both in and out, during a specific period. In businesses, cash flow can come from three different activities:
Competitive advantage is a company's ability to produce goods or services better than its competitors. Having a competitive advantage leads to larger profit margins and increased value for investors and shareholders.
Crowdfunding is the practice of funding a new business venture using small amounts of capital from many individuals. It often utilizes social media and crowdfunding websites like Kickstarter or Indiegogo.
Expenses are costs incurred through the running of a business, including wages, utilities, rent, depreciation, interest, taxes, fuel, advertising, etc. They fall into two categories:
Intellectual property refers to non-physical property created by original thought. This includes things like inventions, literary works, design rights, logos, trademarks and color marks, trade secrets, and computer software. Intellectual property is protected by law.
A joint venture is a business arrangement in which two or more parties collaborate and share ownership, risk, and reward. Joint ventures may be temporary or long-term, and the parties don't need to hold an equal share in the business.
A legal entity is any business or organization with legal rights and responsibilities. Legal entities can pay taxes, enter into contracts, be held accountable for debts, and sue or be sued.
Liabilities are the financial obligations and debts of a business. They decrease a company's value and include payroll, rent, utilities, credit card debt, loans, and accounts payable.
A limited liability company (LLC) is a U.S. business structure that protects business owners (individuals or a group of people) from personal responsibility for debts. LLCs are a hybrid between a corporation and a sole proprietorship.
Minimum viable product is a product development technique in which a new product is developed in its most pared-down version, distributed to early adopters, and refined through customer feedback to full development. The MVP technique allows startup businesses to test how well their product meets customer needs before investing in full-scale production.
Net loss is when a company's expenses exceed total revenue for a given period.
Net profit is the measurement of a company's profit after subtracting all expenses, taxes, interest, and depreciation from total revenue. This is different from gross profit, which is a company's profit after subtracting manufacturing and selling expenses from total sales.
When the net profit value is negative, the company has a net loss.
Revenue is money generated by a company from the sale of goods and services. Unlike income or profit, revenue is calculated without subtracting expenses or liabilities. Another term for revenue is "sales."
Profit margin measures the ratio between the amount of money the company makes per sale versus the amount of money the company spends per sale. The calculation is as follows:
(Revenue - Expenses) / Revenue = Profit Margin
The resulting profit margin value is a decimal that is then converted to a percentage. For example, let's say a company spends $930,000 annually on production and business expenses. They pull in $1 million annually in sales. Their profit margin is as follows:
($1,000,000 - $930,000) / $1,000,000 = .07 (a 7% profit margin)
Generally, a higher profit margin indicates a more successful business.
Return on investment (ROI) is a metric used to evaluate the profitability of an investment. ROI compares how much you invested against how much you earned.
Entrepreneurs and venture capitalists can use ROI to evaluate the performance of their business portfolios. Businesses can also use it to evaluate expenses, like comparing the cost of advertising against the income from ad-generated sales.
Scalability in business refers to the ability of a company to meet fluctuating market demands.
If market demand increases, a business might see an increase in sales volume. In this situation, a scalable company can maintain or improve its profit margin without sacrificing efficiency and streamline its services to support new customers.
If market demand decreases, a scalable company can maintain its profit margin by managing production to avoid inventory overages while maximizing resources and talent.
Social entrepreneurship is the development of a business to address social issues and positively impact a specific community or the world at large. Unlike a non-profit, social entrepreneurship is for-profit.
Some examples of prominent social entrepreneurs include Blake Mycoskie, founder of TOMS Shoes; Scott Harrison, founder of charity: water; Jeffrey Hollender, co-founder of Seventh Generation; and Shiza Shahid, co-founder of the Malala Fund.
A sole proprietorship is an unincorporated business owned by a single person. The business is legally tied to its owner, and the owner is responsible for all debts and liabilities. Any business income is taxed on the owner's personal income taxes.
Sole proprietorships may operate under a business name other than the owner's legal name, but the business remains legally tied to the individual owner.
A target market is a group of potential customers for a startup or existing business. It usually includes people who share demographic markers, such as age or socio-economic status, as well as lifestyle or core values.
Identifying a target market is one of the first steps in entrepreneurship. It can help guide sales decisions, from product development to package design to marketing campaigns.
Valuation determines the present financial value of a company, investment, or asset. This can help businesses attract investors, obtain funding, evaluate ownership shares, resolve tax issues, settle legal disputes, and prepare it for sale to a new owner.
A value proposition is a simple statement on the greatest benefit your product or service offers the customer. A strong value proposition will identify customer needs and how a product or service meets them better than any other.
Businesses communicate value propositions to customers via company websites, advertisements, and digital or print marketing.
Venture capital is a form of private equity that funds startups and early-stage small businesses with the potential for significant growth. Venture capital investors usually offer equity in return for minority ownership of the company. Investors often serve in a managerial role, offering mentorship and guiding growth.
If you have an entrepreneurial spirit and want to start a business venture, you first need to originate a business idea. Start by exploring different industries, doing thorough market research, and identifying gaps in customer needs.
Once you have an original business idea, identify your target market and create a business model canvas. As you further define your business model, detail potential expenses and revenue in a business plan. You will also want to take any necessary steps to protect your intellectual property.
The next step is to secure funding. Depending on which route you want to take, you can visit financial institutions, seek angel investors, or research venture capital funds. You may also want to gather a network of support composed of friends, family, professionals, partners, vendors, and advisors who can offer professional, emotional, and administrative support.
Once you obtain funding and begin to build your startup, you will need space to grow your business. Consider looking for business incubators where you can share space with other business owners at minimal expense. Once you officially open your doors, begin marketing in earnest and building your team.
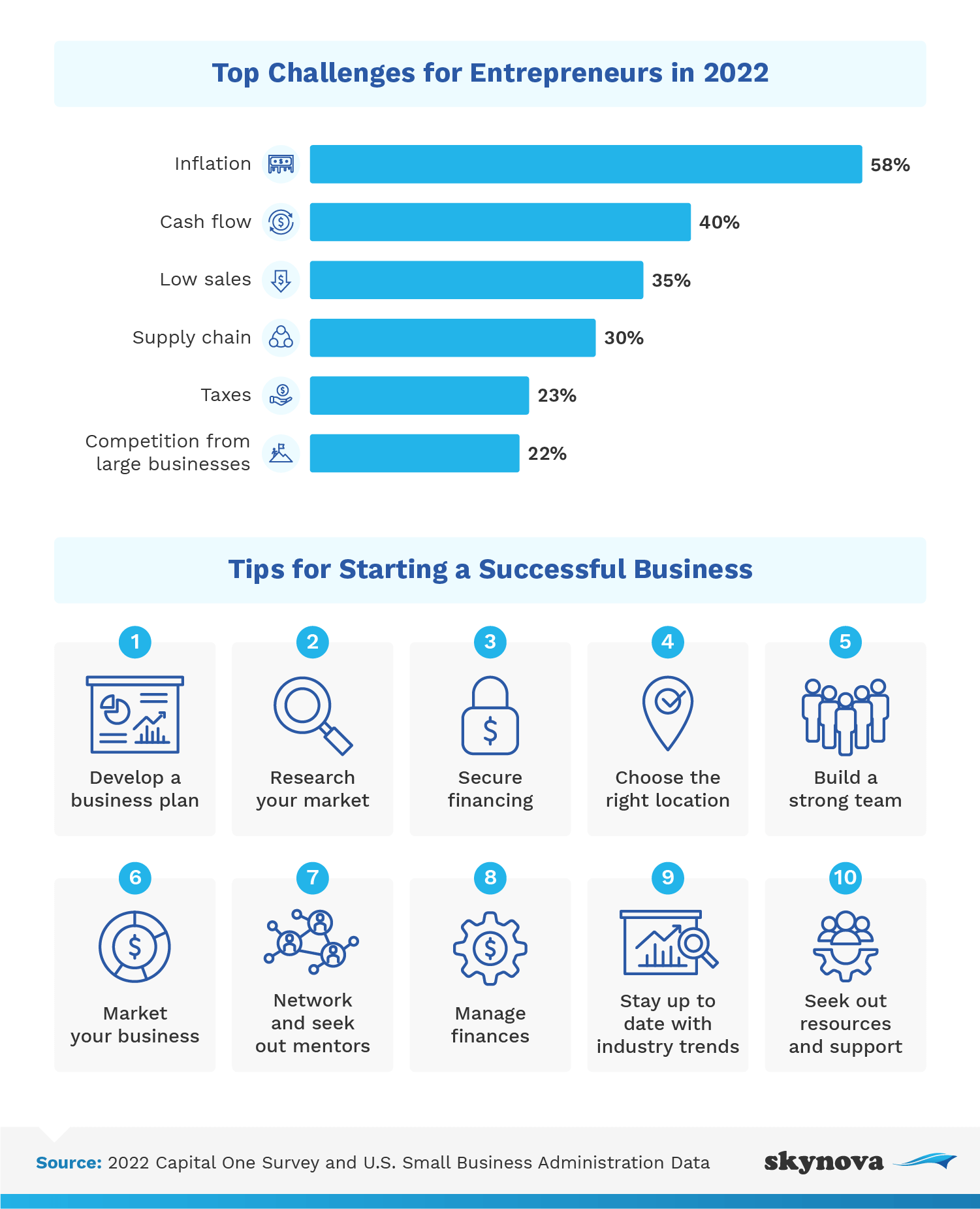
From the early stage onward, manage business finances carefully, hiring people to help if necessary. Adjust expenses and pricing to help offset unexpected costs, inflation, low sales, or other challenges. And make sure to stay on top of industry trends to keep your product and business relevant.
Finally, have patience. Being an entrepreneur and growing a business is hard work. It takes most businesses three to four years to become profitable. But, if your entrepreneurial endeavor succeeds, you'll have the satisfaction of watching your innovation grow from a simple idea into a fully-fledged business.
There are many successful examples of entrepreneurship. But no matter how ambitious your entrepreneurial spirit may be, everyone needs strong support.
Skynova can support your startup or growing business with online invoicing tools. With an invoice template and templates for estimates, bills of sale, packing slips, receipts, credit notes & more, let Skynova streamline your billing process and keep your revenue rolling in.
Know someone contemplating becoming an entrepreneur? You're welcome to share this guide as long as you provide a link to this page. Sharing this information is permissible for noncommercial purposes only.